A shipment network directs its freight to a new path to meet an approaching storm in the middle of the night all without human direction. A cancer care plan is updated by a medical AI assistant in hours after some new clinical trials results are published. This is not pie in the sky visions of the future- these are live current affairs of Agentic AI use.
An agentic AI is a revolution in the field of artificial intelligence. It changes the paradigm of the reactive models to the autonomous, intelligent systems that could develop a plan, execute the tasks and learn during execution in real-time. As businesses are becoming more competitive and employ the tools of innovation, adaptation, and scale, Agentic AI provides the progressive prospective solution to problems in spheres of healthcare, finance, education, and beyond.
Introduction
An agentic AI is a type of sophisticated artificial intelligence software having the ability to perform with a high level of autonomy. Those systems can sense purposes, choose the appropriate tools or information, take actions in order to accomplish the intentions (and they are able to change continuously, according to the feedback of their environment).
As opposed to traditional AI that responds to instructions, Agentic AI takes the initiative, creatively schedules activities, and automatically corrects itself depending on the situation. It is a paradigm shift with significant implications to the way we construct and communicate with AI systems, and it integrates deep learning, reinforcement learning, planning and memory into coherent goal-driven systems.
This blog is divided into five major themes that will help you to read it:
- Understanding Agentic AI – Defining what sets agentic systems apart from traditional AI.
- Applications Across Industries – Exploring how these intelligent agents are transforming healthcare, finance, logistics, and more.
- Social Good and Ethics – Highlighting the importance of ethical frameworks and responsible innovation.
- Technical Guide for Data Scientists – Offering a roadmap and tools to start building and deploying agentic AI systems.
- Conclusion – Reflecting on the future potential and our responsibility in shaping it.
1. Understanding the Foundations of Agentic AI
Fundamentally, Agentic AI designates intelligent systems, which possess the property of the so-called agency, i.e., can make decisions and take actions, as well as modify them based on environmental feedback. Such systems are self-sufficient and proactive in their agenda of achieving instead of answering some unrelated queries.
Agentic AI is built upon several foundational technologies:
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Enable natural language reasoning and contextual understanding.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): Empowers adaptive decision-making over time.
- Planning Algorithms: Allow for multi-step task execution and re-prioritization.
- Memory Modules: Retain historical context to guide future actions.
All the other popular frameworks such as LangChain, AutoGPT, BabyAGI, and CrewAI also illustrate the use of agentic architectures because those structures allow the usage of tools and the introduction of feedback loops and autonomous decisions.
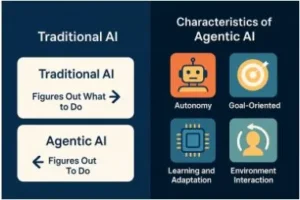
Figure 1: Visual comparison of Traditional AI vs Agentic AI.
2. Applications Across Industries
Agentic AI is rapidly transforming operations in both digital and physical domains. Some prominent examples include:
- Healthcare: AI agents support physicians by reviewing medical history, suggesting diagnoses, and tailoring treatment plans.
- Finance: Agentic systems detect fraud in real-time and autonomously block suspicious transactions.
- Customer Service: Intelligent agents personalize interactions, resolve issues, and escalate when necessary.
- Logistics: AI-powered agents optimize routing for delivery fleets in response to traffic or weather changes.
- Cybersecurity: Autonomous systems identify anomalies, respond to threats, and adapt strategies in milliseconds.
These implementations deliver not just efficiency but also resilience in high-stakes environments.

Figure 2: Sector-wise deployment of Agentic AI.
3. Social Good and Ethical Dimensions
While Agentic AI offers immense promise, it must be developed and deployed with a commitment to ethical principles and the public good.
Applications for Social Impact:
- Climate Action: Monitoring environmental changes and predicting ecological threats.
- Education: Delivering personalized, real-time feedback in low-resource settings.
- Disaster Response: Coordinating aid delivery and evaluating damage in post-disaster areas.
Ethical Considerations:
- Bias and Fairness: Mitigating historical data bias to ensure equitable outcomes.
- Transparency: Designing systems that provide understandable explanations for their actions.
- Accountability: Establishing clear responsibility for agent decisions and consequences.
Safety and Oversight: Embedding safeguards, including human-in-the-loop protocols and behavior audits.
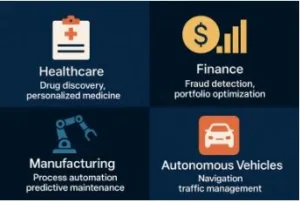
Figure 3: Ethical considerations while designing autonomous AI systems.
4. Technical Guide for Data Scientists
Data scientists eager to explore agentic systems should consider this roadmap:
- Build Strong Foundations: Master LLMs, NLP techniques, and reinforcement learning principles.
- Experiment with Frameworks: Leverage tools like LangChain, CrewAI, and HuggingGPT to create custom agents.
- Integrate External Tools: Extend capabilities using APIs, search engines, and domain-specific plugins.
- Design for Memory: Use vector databases and memory chains to enable long-term context handling.
- Ensure Observability and Safety: Log actions, monitor outcomes, and include mechanisms to intervene when necessary.
The open-source ecosystem is rapidly evolving, enabling developers to build robust, transparent, and safe AI agents from the ground up.
5. Conclusion: Steering the Future Responsibly
Agentic AI is the new frontier in artificial intelligence, characterized by a combination of autonomy, context-sensitivity, decision-making, and flexibility. However, this power has to be directed by principles, which belong to human values.
A data scientist and technologist like us has a moral imperative to engineer systems that serve beyond just working. Through active governance, transparency, and alignment, it will be possible to generate agentic systems that scale the human potential rather than substitute it.
Let us not only fantasize about how to have intelligent agents, but rather construct one that is ethical, inclusive, and sustainable.


